{Important topics for creating different use case diagrams,activity diagrams,class diagrams etc.}
What is UML?
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a graphical language for visualizing,
specifying, constructing, and documenting the artifacts of a software-intensive system.
The UML offers a standard way to write a system's blueprints, including conceptual
things such as
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a graphical language for visualizing,
specifying, constructing, and documenting the artifacts of a software-intensive system.
The UML offers a standard way to write a system's blueprints, including conceptual
things such as
- activities
- actors
- businessprocesses
- databaseschemas
- (logical) components
- programminglanguage statements
- reusable softwarecomponents."
UML provides elements and components to support the requirement of complex systems. UML follows the object oriented concepts and methodology. So object oriented systems are generally modeled using the pictorial language.
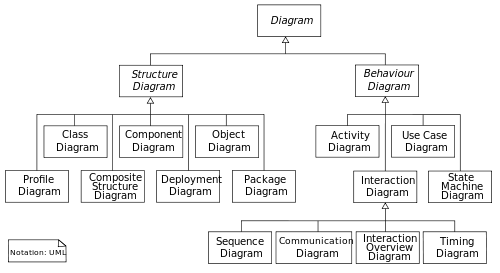
UML 2.2 has 14 types of diagrams divided into two categories. Seven diagram types representstructural information, and the other seven represent general types of behavior, including four that represent different aspects of interactions. These diagrams can be categorized hierarchically as shown in the following class diagram.
Structure diagrams
Structure diagrams emphasize the things that must be present in the system being modeled. Since structure diagrams represent the structure, they are used extensively in documenting the software architecture of software systems.
- Class diagram: describes the structure of a system by showing the system's classes, their attributes, and the relationships among the classes.
- Component diagram: describes how a software system is split up into components and shows the dependencies among these components.
- Composite structure diagram: describes the internal structure of a class and the collaborations that this structure makes possible.
- Deployment diagram: describes the hardware used in system implementations and the execution environments and artifacts deployed on the hardware.
- Object diagram: shows a complete or partial view of the structure of an example modeled system at a specific time.
- Package diagram: describes how a system is split up into logical groupings by showing the dependencies among these groupings.
- Profile diagram: operates at the metamodel level to show stereotypes as classes with the <<stereotype>> stereotype, and profiles as packages with the <<profile>> stereotype. The extension relation (solid line with closed, filled arrowhead) indicates what metamodel element a given stereotype is extending.
Behavior diagrams
Behavior diagrams emphasize what must happen in the system being modeled. Since behavior diagrams illustrate the behavior of a system, they are used extensively to describe the functionality of software systems.
- Activity diagram: describes the business and operational step-by-step workflows of components in a system. An activity diagram shows the overall flow of control.
- UML state machine diagram: describes the states and state transitions of the system.
- Use Case Diagram: describes the functionality provided by a system in terms of actors, their goals represented as use cases, and any dependencies among those use cases.
Interaction diagrams
Interaction diagrams, a subset of behavior diagrams, emphasize the flow of control and data among the things in the system being modeled:
- Communication diagram: shows the interactions between objects or parts in terms of sequenced messages. They represent a combination of information taken from Class, Sequence, and Use Case Diagrams describing both the static structure and dynamic behavior of a system.
- Interaction overview diagram: provides an overview in which the nodes represent communication diagrams.
- Sequence diagram: shows how objects communicate with each other in terms of a sequence of messages. Also indicates the lifespans of objects relative to those messages.
- Timing diagrams: a specific type of interaction diagram where the focus is on timing constraints.